Introduction
Cold wallets aren’t just another crypto accessory — they’re the reason millions haven’t vanished into the hands of hackers.
Every year, billions in crypto are lost forever. Not from bad trades. Not from market crashes. From something far simpler: leaving assets online, exposed, and waiting to be stolen.
Exchanges get breached. Hot wallets get hijacked. One click on the wrong link and your entire portfolio can disappear — instantly.
That’s why serious crypto holders use cold wallets: offline, hacker-proof storage that keeps your private keys where no one can reach them.
This guide isn’t about theory. It’s what the smartest investors and institutions are doing right now to lock down their Bitcoin, ETH, and altcoin stacks.
You’ll learn how cold wallets actually work, how to set one up the right way, and how to avoid the rookie mistakes that lead to permanent loss.
Because in crypto, there’s no customer support. Just what you prepare for… or what you lose.
Key Takeaways
- Cold wallets store your crypto offline — making them virtually immune to online hacks, malware, or exchange failures.
- They’re the gold standard for long-term storage, used by pros, institutions, and anyone serious about protecting their assets.
- Options include hardware wallets, paper wallets, deep cold storage, and even vault-secured setups used by funds and custodians.
- While incredibly secure, cold wallets come with zero room for error: lose your recovery phrase, misplace the device, or skip a step — and your funds are gone.
- This guide breaks down everything you need: wallet types, setup steps, common mistakes, and how the pros actually store millions in digital assets without flinching.
🔐 What Is a Cold Wallet (and Why You Need One Now)
Most people don’t realize it until it’s too late: the moment your private key touches the internet, it’s exposed.
A cold wallet is the fix — a crypto wallet that stores your private keys completely offline. No Wi-Fi, browsers and no background processes silently leaking your future. Just airtight, physical isolation.
Unlike hot wallets (the apps and browser extensions people casually use every day), cold wallets never connect to the internet. That means no phishing, no remote access, no “oops” moment that drains your account while you’re asleep.
This is why serious investors, hedge funds, and early adopters with seven-figure stacks all use cold wallets. Not because it’s trendy — because it’s the only method proven to block modern threats.
And here’s the kicker: cold wallets aren’t just for whales. If you hold more than a few hundred dollars in crypto, you’re already carrying enough risk to justify going offline.
Because once someone has your key, it’s over. There’s no undo button. No chargebacks. No support tickets. Just silence.
So the real question isn’t if you need a cold wallet.
It’s how much unprotected crypto you’re willing to risk without one.
⚔️ Cold Wallet vs. Cold Storage vs. Hot Wallet: What’s the Difference?
If you’re confused by crypto wallet terminology, you’re not alone and that confusion is exactly what leads people to lock up their coins… and still get robbed.
Let’s start with the one most people use — and most people regret:
🔥 Hot Wallet
A hot wallet is any wallet connected to the internet.
Think browser extensions like MetaMask.
Think mobile apps like Trust Wallet or Coinbase Wallet.
Even exchanges count if you haven’t moved your funds.
They’re fast. Convenient. Easy to use. But here’s the brutal truth: they’re also wide open to phishing attacks, malware, SIM swaps, DNS hijacks, clipboard viruses, and every other dirty trick in a hacker’s arsenal.
If someone gets access to your phone, your email, your backup codes — it’s game over.
Hot wallets are great for small, frequent transactions. But for long-term holdings? They’re basically a ticking time bomb.
❄️ Cold Wallet
A cold wallet is the device or method that stores your private keys offline — completely disconnected from the internet.
It could be:
- A hardware wallet like a Ledger or Trezor
- A piece of paper with your seed phrase printed on it (a paper wallet)
- An encrypted USB key stored in a safe
The key idea? No digital exposure.
Even if someone sends a virus to your laptop, your private keys stay untouched. You sign transactions offline, then broadcast them separately.
It’s not just more secure. It’s mathematically unbreakable — as long as you don’t lose it or screw up the setup.
🧱 Cold Storage
Cold storage is the full strategy, not just the tool.
Think of it like this:
- A cold wallet is the safe.
- Cold storage is the entire security plan: where that safe is located, how many backups exist, how they’re stored, who has access, and what happens if something goes wrong.
Cold storage can include:
- Fireproof safes
- Geographically separated backups
- Metal seed phrase engravings
- Multi-signature schemes
- Custodians with legal frameworks
It’s what hedge funds, exchanges, and high-net-worth individuals use to manage millions without trusting a single point of failure.
🧠 TL;DR
Feature | Hot Wallet | Cold Wallet | Cold Storage |
Internet Connected | Yes | No | No |
Use Case | Daily transactions | Long-term storage tool | Full offline security system |
Convenience | High | Medium | Low (but very secure) |
Security Risk | High | Very Low | Minimal (if managed well) |
Common Examples | MetaMask, Trust Wallet | Ledger, Trezor, Paper | Vaults, Metal backups, Custodians |
Mess this up, and you might think you’re secure… until you’re not.
Understand the difference, and you’re already ten steps ahead of the average investor.
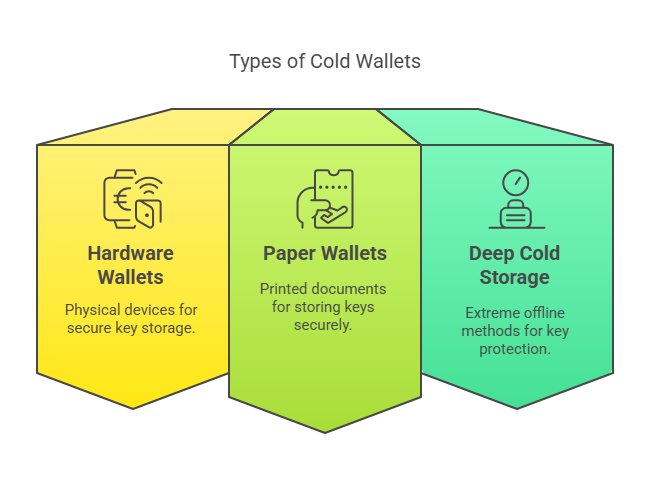
🧰 Types of Cold Wallets (and Which Ones Pros Trust)
Not all cold wallets are created equal.
Some are sleek, battle-tested devices with military-grade encryption. Others are DIY solutions that require zero tech but total discipline. What they all share is this: your private key stays offline.
Let’s break down the options — and what kind of user each is actually for.
1️⃣ Hardware Wallets (Most Popular, Most Trusted)
Hardware wallets are physical devices built for one job: keeping your private keys off the grid.
They connect briefly to your computer or phone to sign a transaction, but your key never leaves the device — and never touches the internet.
The best models are tamper-resistant, PIN-protected, and include secure chips that isolate your credentials from everything else.
Pros trust these because:
- They balance security with usability
- Recovery is possible if lost (as long as you have your seed phrase)
- They support multi-coin portfolios (Bitcoin, ETH, stablecoins, NFTs, and more)
Top Picks:
- Ledger Nano X – Bluetooth-enabled, supports over 5,000 assets
- Trezor Model T – Open-source firmware, touchscreen interface
- SafePal S1 – Fully air-gapped, QR-code transactions only (no USB or Bluetooth)
2️⃣ Paper Wallets (Old-School, High-Risk if Mishandled)
A paper wallet is exactly what it sounds like: a printed sheet with your public address and private key — often in the form of QR codes.
It never connects to the internet, which makes it immune to remote hacking… but it also makes it terrifyingly fragile.
One fire, one water spill, one toddler with a crayon — and it’s gone forever.
Use this only if:
- You’re storing a small amount
- You have a bulletproof physical backup plan (lamination, safes, multiple copies)
- You fully understand how to generate and verify a wallet offline
3️⃣ Deep Cold Storage (For Institutions, Maximalists & Control Freaks)
This goes way beyond hardware or paper.
Deep cold storage refers to long-term, high-security offline systems — think seed phrases engraved on steel plates, stored in geographically-distributed vaults, often behind biometric access and legal safeguards.
Used by:
- Crypto exchanges
- Hedge funds
- High-net-worth individuals holding 6+ figures in digital assets
Deep cold storage often includes:
- Metal wallets like Cryptosteel Capsule or Billfodl
- Vault storage services like BitGo, Coinbase Custody, or Fireblocks
- Multi-signature systems where multiple devices or people must approve a transaction
4️⃣ Air-Gapped Devices & USB Drives (Advanced DIY — Not for the Faint of Heart)
An air-gapped wallet is a completely offline computer or device that never connects to the internet. It’s used to generate and sign transactions, which are then manually transferred to an online device for broadcasting.
Some users also use encrypted USB drives to store wallet files — but these come with serious risk if you don’t understand encryption, key management, or OPSEC.
Best for:
- Tech-savvy users who want full control
- Developers, privacy maximalists, or self-custody purists
Not recommended for beginners. One misstep, and you’re locked out of your own money — permanently.
Each type has a place. What matters most is choosing the right level of protection for your situation — and knowing how not to mess it up.

⚙️ How Cold Wallets Work: Behind the Scenes
Most people think a cold wallet is just a device you stash in a drawer. But what makes it secure isn’t where you put it — it’s how it handles your private key.
Here’s what’s really happening when you use a cold wallet — and why hackers can’t touch it, even if they have your computer, email, or IP address.
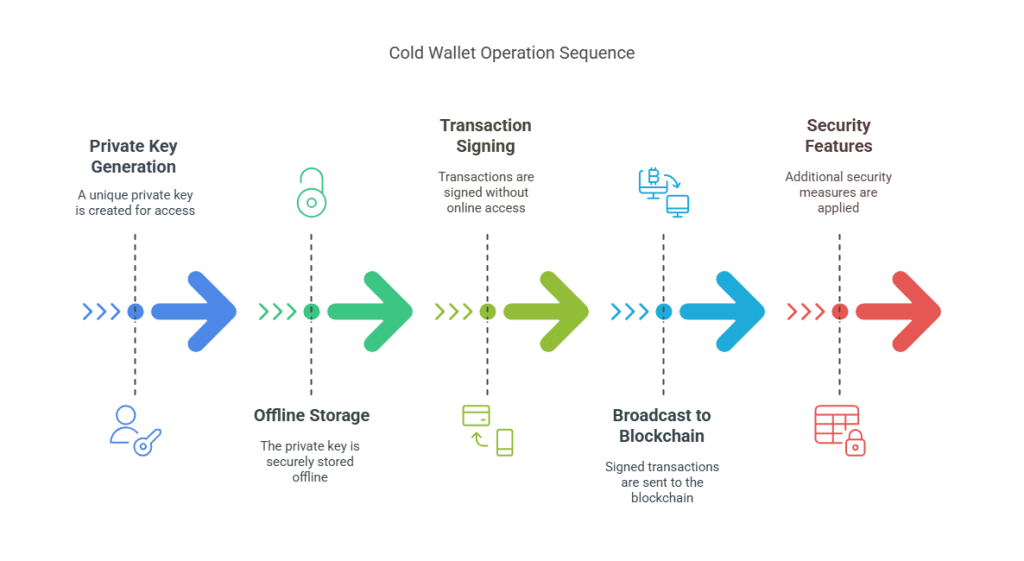
🔑 Private Key Generation
When you set up a cold wallet, it generates a unique cryptographic key pair: a public key (your address) and a private key (your access). This happens inside the device, completely offline.
That private key is the master key to your funds. And once it’s created, it never leaves the device — not even when you’re making a transaction.
🧾 Transaction Signing (Offline)
Want to send crypto? Here’s the genius part: you don’t need to bring your key online.
Instead, cold wallets use a two-step flow:
- You prepare the transaction on your computer or phone (no signing yet).
- You transfer that transaction to the cold wallet — via USB, Bluetooth, or QR code — where it’s signed offline.
- The signed transaction is then sent back to your online device and broadcast to the blockchain.
Your private key? It never touches the internet. It never even leaves the hardware.
🔐 Security Features That Matter
Top-tier cold wallets add multiple layers of defense:
- PIN codes: Block physical access
- Passphrases: Optional extra words that unlock hidden wallets
- Biometric access: Some wallets require fingerprint scans
- Tamper-proof hardware: If someone tries to crack the device, it wipes itself
Even if someone physically steals your wallet, they still can’t spend your crypto without your PIN, your seed phrase, or both.
🧠 The Bottom Line?
Cold wallets don’t just “store” your crypto. They trap the keys inside a sealed cryptographic fortress, let you send funds without exposure, and make remote attacks practically impossible.
You don’t trust the cloud or the browser. You trust math, air gaps, and hardware that’s designed to do one thing — and do it right.
⚖️ Pros and Cons of Cold Wallets
Cold wallets are the gold standard for crypto security — but they’re not magic. If you use them right, they’re bulletproof. Use them wrong? You can lose everything without a single hacker touching your system.
Here’s what you gain — and what you risk.
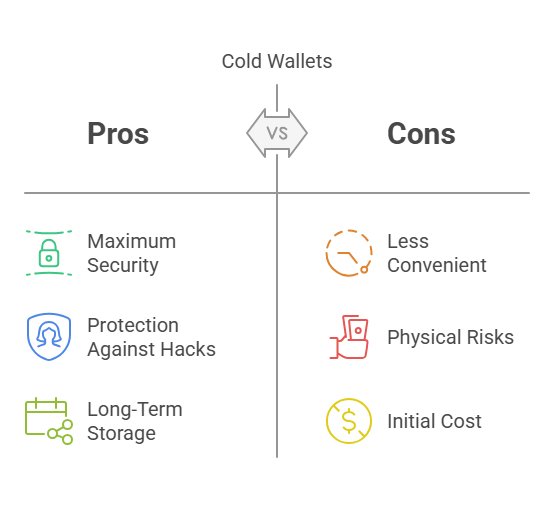
✅ Pros: Why Cold Wallets Are Trusted by the Smartest in Crypto
- Maximum Security
Your private keys are never online. That alone eliminates 99% of threats that wreck hot wallet users every day.
- Immune to Hacks, Phishing & Exchange Breaches
Cold wallets don’t care if Binance gets hacked or if your email gets phished — your keys are sealed off from all of it.
- Ideal for Long-Term Storage
Cold wallets are perfect for holding large amounts of crypto for months or years without touching it. No app updates. No DNS issues. Just peace of mind.
- Full Ownership
Not your keys, not your coins? With cold wallets, the keys — and the power — are yours. Not a third-party’s. Not an exchange’s.
❌ Cons: Where Cold Wallets Can Go Fatally Wrong
- Less Convenient
Want to send crypto fast? Cold wallets add steps: connect the device, sign the transaction, broadcast it manually. No tap-to-send convenience here.
- Physical Risk
Lose the wallet. Trash the wrong USB. Damage the paper backup. If you don’t have the recovery phrase… your crypto is gone forever.
- Recovery Depends Entirely on You
There’s no “reset password” button. If you forget your PIN or misplace your seed phrase, no one — no one — can help you.
- Cost Upfront
Hardware wallets cost $50 to $200+. Paper wallets are free, but fragile. Institutional storage? Thousands per year. But what’s that compared to losing everything?
🔥 Bottom Line?
Cold wallets don’t forgive carelessness. But for those who take security seriously, they’re the ultimate weapon against theft, fraud, and digital disaster.
Still curious? Let’s walk through exactly how to set one up — the right way.
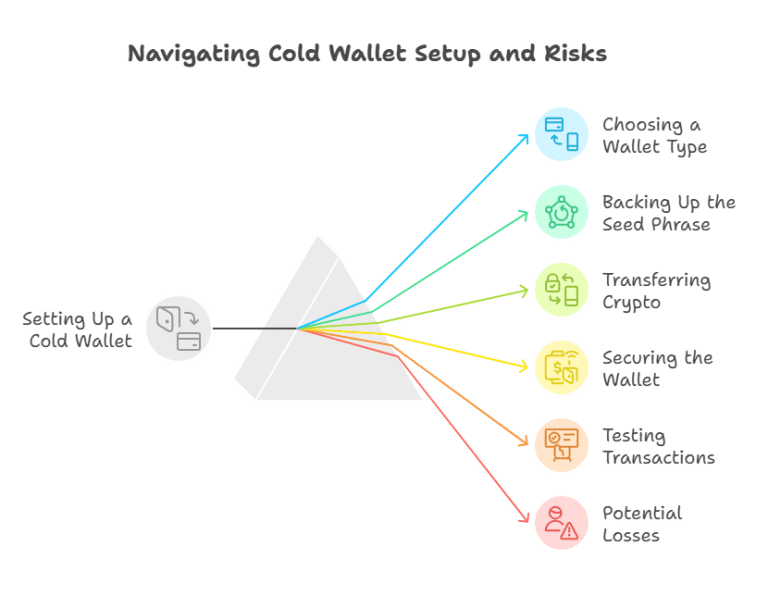
🛠️ Step-by-Step: Setting Up a Cold Wallet Safely
Cold wallets don’t just protect your crypto — they force you to take full responsibility. That’s why setup is everything.
One skipped step… and your entire stack could be unrecoverable.
Here’s how to do it right — no shortcuts, no guesswork.
1. Choose the Right Wallet Type
Pick the tool that fits your needs and skill level:
- Ledger Nano X or Trezor Model T – Great for most users; supports many coins.
- SafePal S1 – Fully air-gapped for maximum isolation.
- Paper Wallet – High risk unless you really know what you’re doing.
- Metal Wallet Backup – Optional, but protects your seed from fire, water, or time itself.
If you’re holding serious amounts of crypto, don’t cheap out here. This is your vault.
2. Generate and Backup Your Seed Phrase
When you first initialize the wallet, you’ll get a 12 to 24-word seed phrase. This is your master key — your reset button if your wallet is lost, destroyed, or stolen.
Write it down. Physically. Not on your phone. Not in a note-taking app. Use pen and paper — or better, engrave it onto a metal plate.
Then:
- Store in a fireproof, waterproof safe
- Consider multiple copies stored in separate, secure locations
- Never take a photo. Never upload it. Never share it — with anyone
3. Transfer Funds from Exchange or Hot Wallet
Send a small test transaction to the new cold wallet address. Wait for confirmation. Verify balance.
Only then should you move larger amounts.
Pro tip: Double-check the receiving address on the wallet screen — not just your computer. Some malware can alter pasted addresses on the fly.
4. Lock Down Your Wallet Access
Set up additional security:
- PIN code
- Optional passphrase (acts like a secret second wallet)
- Hidden wallets (supported by some devices for plausible deniability)
- Device name and pairing lock (to prevent unauthorized USB connections)
You want layers. Not just protection from strangers — but from your future self forgetting something critical.
5. Test Recovery (Before You Need It)
Before you trust the setup with your life savings, run a full recovery test:
- Wipe the device
- Restore it using your seed phrase
- Confirm your funds are visible and spendable
Only then should you consider the job “done.”
Cold wallets don’t give second chances. You either get the setup right — or you find out the hard way.
Now that you’ve got it configured, let’s pull back the curtain on how institutions and crypto veterans store millions without blinking.

🏦 How Pros Store Millions: Institutional Cold Storage Secrets
If you think crypto security is just a Ledger in a drawer… you’re not thinking big enough.
The people and firms managing millions — even billions — in digital assets don’t just rely on cold wallets. They build cold storage systems so layered, so paranoid, so physically and legally locked down, it makes bank vaults look casual.
Here’s how the pros actually do it.
🔐 Multi-Signature Wallets (Multi-Sig)
Instead of relying on a single private key, institutions use multi-signature setups, where multiple people or devices must approve a transaction.
Example:
- A 3-of-5 multisig setup means any 3 of 5 keys are needed to move funds.
- One key might be stored on a hardware device in Switzerland, another in a legal firm’s safe, another in an encrypted USB in a separate continent.
This prevents:
- Rogue employees from stealing funds
- A single point of failure
- Accidental losses due to death or incompetence
It’s paranoid — and that’s the point.
🧊 Geographic Distribution of Keys
Redundancy matters. A cold storage setup holding institutional funds might split seed phrases or keys across:
- Different continents
- Fireproof vaults
- Air-gapped computers stored in secure facilities
- Legal entities governed by smart contracts or signed agreements
One location being compromised isn’t enough to unlock anything.
🧱 Physical Vault Storage with Legal Protections
Services like BitGo, Coinbase Custody, and Fireblocks offer enterprise-grade storage that includes:
- Biometric access
- 24/7 surveillance
- Hardware security modules (HSMs)
- Insurance coverage for stored assets
- Audited recovery protocols
These solutions don’t just protect coins — they protect reputation, clients, and regulatory compliance.
💀 Disaster Recovery Plans (Seriously)
Every good setup includes a what-if plan:
- What if someone dies?
- What if a natural disaster wipes out a safe house?
- What if one signer goes rogue?
Pros simulate these scenarios before they happen, not after. And they often use dead man’s switches, time-locked contracts, or trustees to ensure continuity.
🧠 So, Should You Do This?
Not unless you’re managing eight figures or run an exchange.
But understanding what the pros do gives you something even more valuable: a benchmark.
You don’t need a biometric vault in Singapore. But you should ask:
- Do I have more than one backup?
- Is someone I trust able to access it if I’m gone?
- Could I restore everything if my house burned down tomorrow?
If the answer to any of those is “I don’t know,” you’re not secure — yet.

☠️ Common Mistakes That Get People Wrecked
Cold wallets are built to eliminate risk — but they don’t protect you from yourself.
Every year, people lose access to life-changing amounts of crypto because they misunderstood one step, got lazy, or thought they were smarter than the system.
Don’t become a cautionary tale. Watch for these cold wallet killers:
❌ 1. Losing the Seed Phrase
This is the #1 reason people lose their funds — permanently.
- They wrote it down… somewhere.
- They meant to back it up later.
- They stored it in one place — and that place burned, flooded, or vanished in a move.
There’s no password reset. If your seed phrase is gone, so is your crypto.
Fix it: Back it up. In multiple places. Physically. Securely. Today.
❌ 2. Storing Your Wallet in a “Safe” Place That Isn’t Safe
Some people leave their hardware wallet in a nightstand.
Others tuck their seed phrase into a book, a drawer, or a password manager.
That’s not security — that’s wishful thinking.
If someone finds it, or your home is compromised, your entire net worth could disappear in minutes.
Fix it: Use a fireproof safe. Use metal backups. Distribute copies to trusted locations. And if you die, make sure someone you trust can recover it — legally and logistically.
❌ 3. Buying Wallets from Third-Party Sellers
eBay. Craigslist. “Discount” crypto shops. All places where you can unknowingly buy a pre-tampered wallet with hidden malware or fake firmware.
Once you load your crypto, the attacker waits… then drains it.
Fix it: Only buy directly from the manufacturer (Ledger, Trezor, SafePal) or an authorized, verifiable source.
Disclaimer: I am an independent Affiliate. The opinions expressed here are my own and are not official statements. If you follow a link and make a purchase, I may earn a commission.
❌ 4. Overcomplicating Your Setup
Some people hear about multi-sig, hidden wallets, decoy phrases, and they try to build Fort Knox — but end up locking themselves out of their own vault.
People forget passphrases. They lose track of which key goes where. They get paranoid… and paralyzed.
Fix it: Complexity is fine — if you fully understand it. Otherwise, start with something simple, secure, and sustainable.
❌ 5. Never Testing Recovery
You wrote down the seed, stored it and you feel safe.
But you never actually tested restoring the wallet — and you don’t even know if your backup works.
By the time you need it, you’ll be panicked… and possibly too late.
Fix it: Run a full recovery test. Now. While you’re calm. While your crypto’s still safe.
The biggest threat to your crypto isn’t hackers. It’s your own false sense of security.

❓Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What’s the best cold wallet for crypto?
If you’re just getting started, Ledger Nano X and Trezor Model T are top-tier picks. They support thousands of coins, offer strong security features, and come from trusted manufacturers.
For a fully air-gapped solution, SafePal S1 is a great option — no USB, no Bluetooth, just QR-code signing.
Can cold wallets be hacked?
Only if you mess up.
A cold wallet, used properly, is virtually unhackable. The key never touches the internet, and transactions are signed offline. But if you expose your seed phrase, buy a tampered device, or store backups carelessly — all bets are off.
How much does a cold wallet cost?
Most hardware wallets range from $50 to $200. Paper wallets are technically free, but carry higher physical risk. Institutional cold storage solutions (like custodial vaults and multi-sig services) can cost hundreds to thousands per year.
What happens if I lose my cold wallet?
If you’ve backed up your seed phrase, you can restore your wallet — and all your funds — on a new device.
If you didn’t back it up properly? You’re out of luck. That crypto is gone.
Is Coinbase a cold wallet?
No. Coinbase Wallet and the Coinbase exchange are both hot wallets. They’re connected to the internet, even if they offer certain security features.
If you want true cold storage, you’ll need to move your crypto to a separate offline wallet that you control.
Should I use a cold wallet even if I only hold a small amount of crypto?
That depends on your tolerance for loss. If your crypto is worth more than a pair of sneakers, ask yourself: would you leave that much cash sitting in a public locker?
Cold wallets aren’t just for whales — they’re for anyone who takes self-custody seriously.

🔚 Final Thoughts: Don’t Store Your Crypto Like a Newbie
You don’t get second chances in crypto.
There’s no bank to call. No password to reset. No “oops” button to undo a stolen transfer. Once your keys are exposed, it’s over — and it’s permanent.
That’s why cold wallets aren’t optional. They’re essential.
Whether you’re holding $500 or $500,000, keeping your private keys offline is the single smartest move you can make. Not someday. Not when you “get around to it.” Now.
Because the people who lose their crypto? They always had good intentions. They always meant to upgrade their setup. And they always thought it wouldn’t happen to them.
Don’t be one of them.
Set up your cold wallet. Back it up. Test it.
Then sleep better than anyone still storing their coins in a browser extension.
Explore more cryptocurrency storage solutions in our Crypto Glossary.

1 thought on “Cold Wallets Exposed: The Real Way Pros Store Millions in Crypto”